
Oct 14 2022

Oct 14 2022

Oct 14 2022

Oct 01 2022
Cartridge Heater selection guide, I want to say a few words:
1) Cartridge Heater is generally non-standard customized, which is selected according to the specific actual usage;
2) The diameter of Cartridge Heater is less than 6mm, the thinner the more expensive;
3) The length of Cartridge Heater is shorter than 50mm, the shorter the more expensive;
4) The higher the surface load of Cartridge Heater, the more expensive the price;
5) The price of inner leads of Cartridge Heater is much higher than that of outer leads;
6) Cartridge Heater's quotation is never calculated by length, and all parameters need to be integrated to make a quotation.
What scenarios are Cartridge Heater commonly used in:
▲ Classification of installation methods: used for embedded mold hole heating, exposed air dry heating
▲Which equipment is used specifically:
Plastic mold industry, packaging and sealing equipment, pharmaceutical molding equipment, 3D hot bending machine equipment, 3D printer equipment, extrusion equipment, ignition equipment, etc.
☑ Single-head electric heating tube selection guide-structure selection
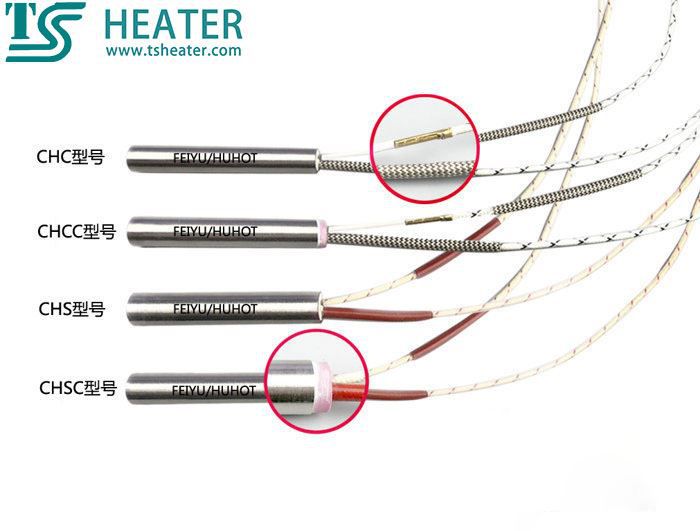

Notes:
CHC model refers to external wiring structure;
CHCC model refers to external wiring + ceramic head structure;
CHS model refers to an inner lead structure;
CHSC model refers to inner lead + ceramic head structure
Cartridge Heater selection guide----technical parameter selection
<
| Tube material | SS304/321/310S/Incoloy 800/840 | ||||
| Heating wire material | Cr20Ni80 | ||||
| Terminal | Copper | ||||
Lead wire | G | silicone glass fiber braided tinned copper wire | 180℃ | ||
| T | Teflon wire | 260℃ | |||
| M | Mica glass fiber braided pure nickel wire | 400℃ | |||
| Heat-resistant temperature of the insulating tube |
180 ℃ | ||||
| Operating temperature | 700 ℃ | ||||
| Model | L | V | W | Wire | |
| Wire Type | Wire Length | ||||
| CHC6 | -40 | V220 | W50 | G | 250 |
Note①: Material selection suggestion:
The surface load is less than or equal to 6W/ cm2. Choose SS304;
6W/cm2<surface load≤12W/cm2. Choose SS321 or SS310S; 12W/cm2 <surface load ≤ 20W/cm2 -. Choose SS310S or Incoloy 800/840
Note ②: The use temperature of 700℃ refers to the use of material SS310S or Incoloy800/840. This temperature is used for a 1-year warranty in an embedded dry burning environment, and 3 months in bare air dry burning environment. [Note that the domestic low-end single-head tube embedded dry-burning is guaranteed for 3 months. Low-cost performance, not recommended. 】
Cartridge Heater selection guide-common sizes. The following sizes and powers are common models. The following models are made of stainless steel 304 or stainless steel 321. Other sizes can be customized non-standard, you can directly consult online customer service.
※ Common dimensions of 6mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 6 | 40 | 220 | 50 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 80 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 100 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 120 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 140 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 150 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 190 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 300 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 400 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 500 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 8mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 8 | 40 | 220 | 70 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 100 | |||||
| 60 | 200 | 130 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 160 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 190 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 220 | |||||
| 100 | 200 | 250 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 400 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 550 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 700 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 850 | |||||
| 350 | 220 | 1000 | |||||
| 400 | 220 | 1100 | |||||
| 450 | 220 | 1200 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 10mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 10 | 40 | 220 | 90 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 130 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 150 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 200 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 220 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 250 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 300 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 450 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 650 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 800 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 1000 | |||||
| 350 | 220 | 1100 | |||||
| 400 | 220 | 1200 | |||||
| 450 | 220 | 1250 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 12mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 12 | 40 | 220 | 110 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 150 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 200 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 240 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 290 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 300 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 350 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 550 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 800 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 1000 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 1200 | |||||
| 350 | 220 | 1300 | |||||
| 400 | 220 | 1400 | |||||
| 450 | 220 | 1600 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 14mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 14 | 40 | 220 | 130 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 180 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 230 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 260 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 300 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 350 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 400 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 600 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 850 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 1100 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 1300 | |||||
| 350 | 220 | 1400 | |||||
| 400 | 220 | 1600 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 16mm pipe diameter
<
Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 16 | 40 | 220 | 150 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 200 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 250 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 300 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 350 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 400 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 450 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 700 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 1000 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 1200 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 1500 | |||||
| 350 | 220 | 1600 | |||||
| 400 | 220 | 1800 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 18mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 18 | 40 | 220 | 160 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 220 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 300 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 350 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 400 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 450 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 500 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 800 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 1200 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 1400 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 1600 | |||||
| 350 | 220 | 1800 | |||||
| 400 | 220 | 2000 | |||||
※ Common dimensions of 20mm pipe diameter
<
| Model | L (length: mm) | V (voltage) | W (power) | Wire | surface load (W/cm2) | ||
| Type | D (pipe diameter) | Wire type | Wire Length (mm) | ||||
CHC/CHS | 20 | 40 | 220 | 180 | G/T/M (CHC generally uses G/T type leads, CHS generally uses M type leads) | Standard 250 | 2≤W/cm2≤12 W/cm2=W/{Dπ(L-15)/100} (Please calculate based on the power density of the heating part (not the full length). |
| 50 | 220 | 250 | |||||
| 60 | 220 | 320 | |||||
| 70 | 220 | 400 | |||||
| 80 | 220 | 450 | |||||
| 90 | 220 | 500 | |||||
| 100 | 220 | 550 | |||||
| 150 | 220 | 1000 | |||||
| 200 | 220 | 1300 | |||||
| 250 | 220 | 1500 | |||||
| 300 | 220 | 1700 | |||||
☑Cartridge Heater selection guide-selection of other accessories
★A selection of accessories: thread
① Cartridge Heater with thread is generally used in the working environment of heating liquid.
② Thread style selection: fastener thread (M), G thread, R thread, NPT thread, etc. Nuts are available.
③Selection of thread position: refer to the style drawing
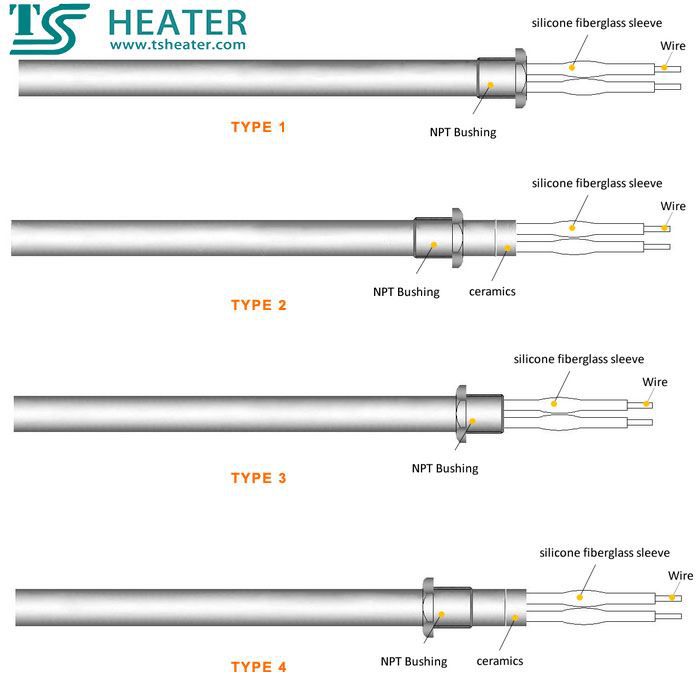
④The choice of thread material: according to the corrosion performance of the heating liquid, stainless steel 201, 304, 316, etc. are generally used
★The second choice of accessories: fixed baffle/flange
①The size and style of the fixed baffle/flange are all non-standard customized, and you can also consult the customer for design.
②Selection of fixed baffle/flange material: According to the corrosion performance of the heating liquid, stainless steel 201, 304, 316, etc. are generally used
★Three options for accessories: lead protection method
①Lead protection method 1: metal hose sheath
②Lead protection method 2: Metal braided sheath
★Four options for accessories: thermocouple
①General style of thermocouple: K/J type thermocouple
②The thermocouple placement position: the bottom of the tube is grounded, the bottom of the tube is not grounded, the middle of the tube is grounded, and the middle of the tube is not grounded.
☑Cartridge Heater selection guide ----- Use attention
▲ The working voltage must be consistent with the rated voltage, and the general working voltage should not exceed 10% of the rated voltage;
▲ In order to ensure that the heat generated by Cartridge Heater can be transferred to the heating medium in time, and reduce the temperature of the internal material of the single-head electric heating tube, the gap between the outer diameter of the heating tube and its insertion hole should be minimized when inserting heating, usually two The gap between them is less than 0.1mm, such as an electric heating rod with a pipe diameter of 10mm, which should be a hole within 10.1; when exposed to air, the surface temperature must be controlled, otherwise, the life will be short;
▲ When inserting heating, when processing the installation hole, the coaxiality and size tolerance should be effectively ensured, if the processing hole is trimmed with a reamer and other tools during processing;
▲ The residue left in the processing, such as organic oil, should be cleaned up before installing the heating rod, which will be carbonized after heating, which will affect the heat transfer ability;
☑Cartridge Heater selection guide-we help you design
If you read the above information, you still can't choose the model, you can directly consult us